- Home
- >
- Offshore News
- >
- 5 Questions About Product Development You Must Ask Yourself
1. When do you need software product development services?
Software Product Development Services provides businesses with new ways to grow, extend their client base, and enter new industries. Here’s when you need to hire software product development services to boost your business.
Release a New Product
You need software product development services when you’re ready to bring a new product idea to market. This is particularly important if you’re looking to tap into new customer bases or provide innovative solutions to existing customers. A tailored software product can differentiate your company in a competitive industry.
Extend and Improve Your Existing Product
If your existing products need enhancement to meet the evolving expectations of your market or to maintain competitiveness, it’s time to consider software development services. Upgrading features, improving performance, and reducing costs are all crucial steps to keep your product relevant and appealing.
Enhance Your Business with Cutting-edge Products
When your business requires a strategic overhaul to improve operational efficiency or decision-making, integrating custom business intelligence tools can be transformative. This is especially relevant if you’re facing increased competition or need deeper insights into your operations and market.
Upgrade Your Legacy Applications to Modern Technologies
Software product development services are necessary when your current systems are outdated and no longer meet industry standards or user expectations. Modernizing your technology can reduce operational costs, enhance security, and improve user experience, making your business more robust and adaptable.
As you assess these needs, a key question about product development to consider is: “How will these services specifically address the unique challenges and opportunities my business faces?” Answering this will help determine the right timing and approach for engaging software product development services.
2. What are the types of software product development services?
When exploring questions about product development, one key inquiry often arises: What types of software product development services are available?
Each type of service caters to different stages and needs in the software creation and enhancement process. Understanding these services is crucial for anyone looking to bring a software idea to life, enhance existing products, or expand their digital offerings. Here’s a closer look at the various software product development services:

2.1 UI/UX Design
This service focuses on the look and feel of your software product. Designers create prototypes and continuously refine the software’s interface and user experience to ensure it is attractive and easy to use. The goal is to make a product that stands out, appeals to users, and builds customer loyalty.
2.2 MVP Development
MVP stands for Minimum Viable Product. This approach helps you take a basic version of your idea and test it in the market to see if people will actually want it. By developing an MVP, you can find out early if your concept has potential, saving time and resources before committing to full-scale development.
2.3 Full-cycle Software Development
This comprehensive service covers all phases of creating a software product—from the initial idea and design through development to the final deployment and maintenance. It ensures that all aspects of the software development process are managed and executed effectively, keeping projects on schedule and within budget.
2.4 Web App Development
This service involves creating applications that run on a web browser. Web apps can be accessed from anywhere and on any device with an internet connection, offering convenience and flexibility. Developers focus on building applications that are fast, innovative, and error-free to enhance the performance of your business online.
2.5 Mobile App Development
Mobile app development is about creating applications specifically for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. These apps are designed to offer unique designs, excellent user functionality, top-notch security, and even functionality without an internet connection (offline mode).
3. How many steps does the software product development process have?
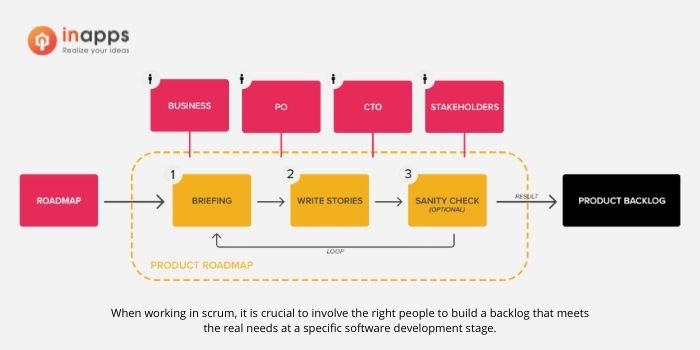
When addressing questions about product development, it’s useful to understand the structured process involved. This process, often called software product development strategy, includes every stage of software development, identifies key stakeholders, sets goals and objectives, and outlines a timeline for the project.
Let’s explore the seven essential steps that take a software product from concept to launch.
3.1 Ideation and Brainstorming
Creating a complete vision for the product or service is the first step in the software product development process. Organizing a brainstorming session or ideation workshop with your team and, if applicable, the software agency you plan to collaborate with is one very productive technique. Your goal is to learn everything you can about the product, including what it aims to provide, how it will meet market demand, and how you intend to set yourself apart from the competition.
3.2 Requirements Gathering & Feasibility Analysis
Now that you know what the software product will offer, it’s time to undertake a feasibility analysis. It is a comprehensive examination of both technical and business issues that can impact the success of your software development project.
This includes details like the anticipated product launch date, the software development budget, essential project milestones, and the expected return on investment. You must guarantee that all parts of your product development have been addressed.
According to ApiumHub, the number one factor that causes software delivery dates to be missed is unreasonable expectations (according to 14.45% of respondents). We can avoid these by putting in the effort before drafting a single design or line of code.
As a result, you should have a Software Requirements Specification document that your designers and developers will use in the next stages by the end of this stage.
3.3 Concept Design & Prototyping
Your designers will immediately start generating early visual designs for your product based on the documentation. They will work on high-fidelity prototypes if you agree with the direction indicated in the wireframes. Once each design module is completed, they will hand over the designs and documentation to the development team.
3.4 Development
The longest stage of the software product development process is development and coding. It’s all about turning product specifications into a usable product. Developers must ensure that the code meets product standards and satisfies stakeholders’ expectations. On the other hand, the coding phase should go well provided all preceding stages were carefully handled, and the programmers ended up with a clear SRS document that they can closely follow.
3.5 Testing
After the software has been created, it must be tested to ensure no defects or errors that make it difficult or impossible to use. This procedure varies each company, but in general, a group of Quality Assurance engineers conducts a series of tests using a range of frameworks and tools, including:
- Testing of functionality
- Acceptance testing for users
- Integration of systems
The major goal of this step is to ensure that the code is clean and that the final product meets business objectives. Only after that will we move on to the implementation and launch phases.
3.6 Implementation and Launch
The freshly produced and tested software is brought to production in this step, guided by an implementation plan. Only specific changes will be deployed if product iterations are required. Depending on the product’s complexity, the iterations can be done as a single release if the project is basic or in stages if the project is more advanced.
3.7 Maintenance
The final stage of the software product development process is maintenance. Its goal is to maintain the software operation, updates, and upgrades. It can be tweaked based on user feedback to ensure that the product functions well. New functionalities can also be implemented during the maintenance stage to satisfy user needs better.
4. How much does a software product development service cost?
One of the most common questions about product development revolves around the costs involved. How much does it actually cost to engage in software product development services? In this product development questionnaire, we’ll break down the various factors that influence the cost of developing a software product, providing a clearer picture of what you might expect to spend.
4.1 Average software development costs
When you embark on a digital project, you or your stakeholders will likely need an initial estimate of the software development costs. It’s important to remember that time is money. Therefore, the costs of your software development project will typically be calculated on an hourly basis.
Additionally, the number of professionals involved and the speed at which you require deliverables or need to meet deadlines also affect the total cost. Another key factor is the platform where your software will be accessible. This means considering on which platforms users will interact with your software.
Below, we provide examples of the estimated number of hours required for software solutions tailored to various platforms. For context, we use an average hourly rate of $50 for software development. This rate is below the average in the United States but above the minimum found in Asia
| Solution | Platform | Time (hrs) | Cost ($) |
| Vehicle insurance app | Web | 15,360 | 768,000 |
| iOS | 1,960 | 98,000 | |
| Android | 1,980 | 98,000 | |
| Banking ERP software | Desktop | 2,400 | 120,000 |
| Web | 5,760 | 288,000 | |
| Healthcare CRM solution | Desktop | 2,510 | 125,000 |
| Web | 5,760 | 288,000 | |
| E-commerce platform | Web | 1,600 | 80,000 |
| Blockchain wallet | Web | 1,440 | 72,000 |
| iOS | 1,500 | 75,000 | |
| Android | 1,530 | 76,500 |
The values provided are just as a guide. Actual figures will vary depending on the extent of the project.
You may also use this easy formula to estimate the weekly cost of development based on the number of developers you hire:
Cost per week = Hourly rate x Hours per week x Number of Developers
The formula works for both in-house hiring and software outsourcing to third-party developers.
4.2 Factors influencing software development costs
Let’s look at three of the most critical aspects that influence software development pricing:
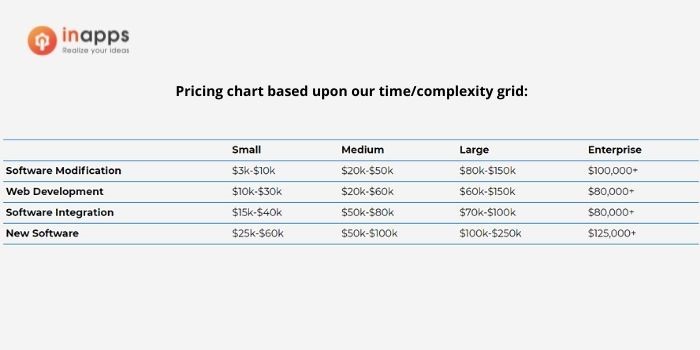
4.2.1 Type of Software Project
Typical software development engagements are divided into the following categories on a high level:
- New software development refers to the creation of new software that is customized.
- Enhancement of existing software (software modification).
- Custom code to add functionality or integrate current software into other processes is known as software integration.
- Custom web-based software development is what web development entails.
Each of these initiatives has a different team make-up and necessitates a different level of development. The first step in producing a cost estimate is understanding the type of project. To establish the final estimate, we will combine this information with the project’s size and project team.
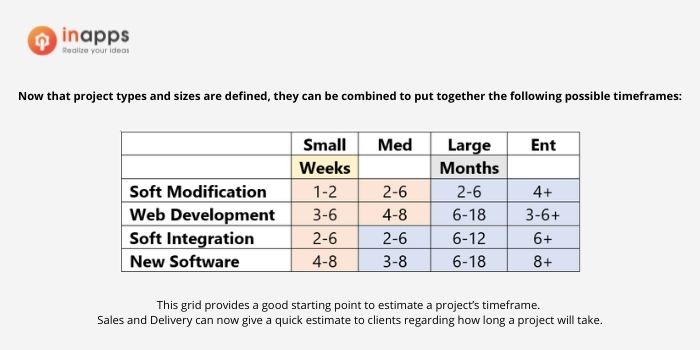
4.2.2 Size of Software Project
The following step is to determine the scope of a project. Size is a bit of a guessing game. The complexity of a project and its size tend to be closely related, but this isn’t always the case. In general, project sizes are classified as follows:
Small product development project
Minor changes are usually involved in a small project. Typically, these are changes to the user interface or bug fixes with a well-defined cause. Interaction with the client is limited, for example, “Is this what you want to do?” followed by “Here is what we did.”
Medium product development project
These engagements are more significant than a minor tweak, but they usually have a well-defined scope of deliverables and are often standalone solutions or integrations. Typically, we are dealing with a single data source. This category includes projects like a small mobile application or a web interface to an existing inventory system. External requirements for client interaction are more stringent than in small projects. It may include a few design sessions, weekly check-ins, and milestone sign-offs.
Large product development project
These solutions are more in-depth and complex. Large projects may necessitate system integration, a database component, and security and logging features. An underlying framework and a module-based design are expected, with scalability and maintainability in mind.
This category would include a multi-party application that works across multiple platforms (iOS, Android, and Web). Extensive design sessions and milestone agreements are among the external requirements for client interaction. Daily calls and interactions with technical team members are standard, followed by weekly status calls with upper-level management.
Enterprise product development project
Enterprise-level projects are almost always built on top of an underlying framework. They have far stricter security, logging, and error handling. Data integrity and security are critical for these mission-critical applications. Though not limited to this category, support systems are designed to be resilient and capable of handling 2-3 concurrent faults in the underlying infrastructure before affecting users.
External requirements for client interaction include fully integrated client and IT teams. Extensive design sessions and milestone agreements across multiple teams; daily calls and interactions with technical team members across multiple groups/disciplines; weekly status calls with higher-level management; quarterly all-hands meetings are all-time requirements.
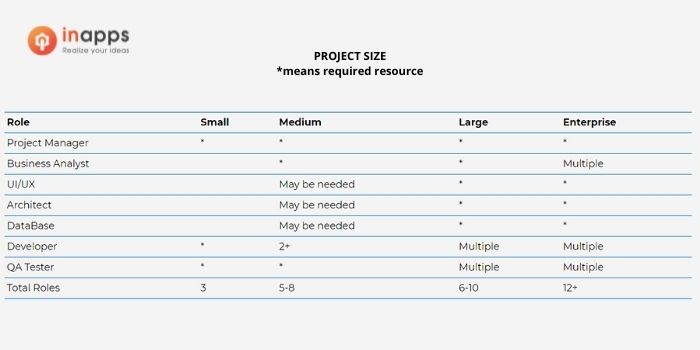
4.2.3 Development Team Size
Once you’ve identified the type and size of your project, the next step is to determine the size of the team needed to execute it. While every project typically requires a Project Manager, a Developer, and a QA Tester, it’s important to note that each role doesn’t necessarily equate to a single team resource. Some team members may fulfill multiple roles, depending on their skills and expertise, allowing for more efficient resource allocation.
For example, in a small project, a Developer may also serve as a tester. In a small/medium project, the Project Manager may also serve as the business analyst. Team personnel usually fulfill only one task for more extensive, complicated projects to efficiently move a project ahead.
Rough estimates of team sizes may include the following structural roles
Let’s use the following numbers to get some rough cost estimates for a team (these prices represent rough costing for quick estimate):
- $1,000/day/developer
- ~$10,000/week/team
We can finally arrive at a project cost by combining the cost of a team with the project time estimates from the chart above.
Learn more: Offshore software development rates by country – detailed comparison.
5. How To Find The Right Software Product Development Partner
After having done some research, you’re likely to have a list of potential software product development companies in mind. Now here comes the important question. How do you single out the right partner for you? Here’s step-by-step guide to help you out.
5.1. Prioritize Your Criteria
Start by figuring out what’s most important for your project. Maybe you need a partner who’s great with a specific technology, or someone who knows your industry well. Knowing your top priorities will help you focus your search. If you’re building a healthcare app, you might prioritize finding a partner with experience in healthcare software development.
5.2. Conduct In-Depth Evaluations:
Now, take a closer look at each potential partner. Check out their past work and what their clients have said about them. Look for examples of projects similar to yours to see if they’ve done good work in the past. You can utilize third-party review platforms, such as Clutch or GoodFirms, to find independent reviews and ratings of your chosen software development companies. These platforms gather feedback from clients and provide unbiased insights into the reputation and performance of each company.
5.3. Schedule Meetings or Workshops
Set up meetings or workshops with the companies you’re interested in. This gives you a chance to talk to them face-to-face and see if you get along well. It’s also a good opportunity to discuss your project in more detail. You can arrange a video call with each potential partner to chat about your project and see if you feel comfortable working with them.
5.4. Ask Specific Questions
During your meetings, don’t be afraid to ask lots of questions. Get into the nitty-gritty details about how they’ll handle your project. Ask about things like how they’ll communicate with you and how they’ll deal with any potential problems. Or ask them how they’ll make sure your app works smoothly on different types of smartphones.
5.5. Evaluate Cultural Fit
Think about whether you’d enjoy working with each potential partner. Consider things like their work style and how well they understand your goals. You want to find someone who’s a good fit for your team. If you prefer a laid-back approach, you might not want to work with a formal and strict partner.
5.6. Consider Scalability and Long-Term Partnership:
Make sure your chosen partner can handle your project as it grows and provide robust post-launch support. You want someone who can grow with you and stick around for the long haul.
Ensure they offer:
- Maintenance and Updates: Regular updates, patches, and bug fixes to keep your software product running smoothly post-launch.
- Technical Support Channels: Availability through various channels for timely assistance with any issues.
- Scalable Support: Capacity to scale support services as your user base grows and your software product evolves.
- Proactive Monitoring: Monitoring services to detect and address potential issues before they affect users.
- Knowledge Transfer: Documentation and knowledge transfer to empower your team to handle routine maintenance tasks.
- Continuous Improvement: A commitment to ongoing improvement and innovation in support services to meet evolving needs.
5.7. Make an Informed Decision
Once you’ve talked to all your potential partners, compare them to see which one comes out on top. Look at things like their strengths and weaknesses to help you make your decision. Making a list of the pros and cons of each partner can help you see which one is the best fit for your project.
After weighing all your options, it’s time to make your decision. Choose the partner that ticks all the boxes and feels like the best fit for your project. However, sometimes, you just have to go with your instincts. If you feel good about a certain partner, that’s probably a sign that they’re the right choice for you. Even if a company looks great on paper, if something feels off during your meeting with them, it’s okay to trust that feeling and keep looking.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to find the right software product development partner for your project without feeling overwhelmed. Trust your instincts, ask lots of questions, and choose the partner that feels like the best fit for you.
Wrapping Up
Whatever project you’re nursing, we hope this blog on 5 key questions about product development serves as a road map for software product development. You now understand the steps and factors to determine before choosing a software product development service. As previously stated, each project is unique; however, clearly understanding these five questions can help you have a good start.
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.