In this versatile world, database systems are also not 100% alike—the way of accessing data differs. When it comes to migration between databases, Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) could be an option if you want to avoid wasting time and effort.
Here are some advantages of ORM over the traditional query approach:
- Developers can only focus on business logic rather than writing interfaces between code and DB.
- Reduces development time and costs by avoiding redundant codes
- Capable of connecting to different databases, which comes in handy during switching from one DB to the other.
- Helps to effectively query from multiple tables similar to SQL JOIN—ORM takes the responsibility of converting the object-oriented query approach to SQL queries.
In this article, we will learn how to make an effective object-relational mapping with Sequelize in Node.js.
There are a couple of other alternatives but this module is my favorite. Sequelize is easy to learn and has dozens of cool features like synchronization, association, validation, etc. It also has support for PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, and MSSQL.
What is an ORM?
Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) is the process of mapping between objects and relational database systems. So it acts like an interface between two systems hiding details about an underlying mechanism.
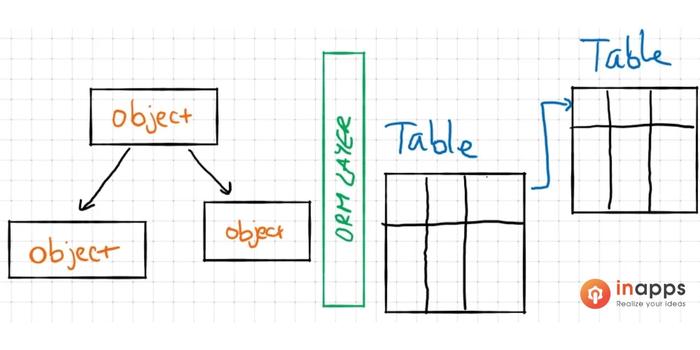
What is object relational mapping
Starter app
So our objective here is to understand its functionality by creating a sample application that will perform some basic operations with CRUD. I assume you have Node.js and PostgresSQL installed.
Let’s use “express application generator” to create a starter application.
npm install express-generator -g
express testappTo install sequelize, postgres and ejs (template engine), navigate to root of your generated folder.
npm install --save sequelize
npm install --save pg pg-hstore
npm install --save ejsWe will use EJS for templating instead of Jade. So we can remove Jade related dependencies and files from the default Express-generated project.
DB connection and models
Connecting to postgres is as easy as a single line
var sequelize = new Sequelize('postgres://username:[email protected]:5432/db_name');Models are the objects which represent tables in a database. They are the heart of ORM and we can define them with sequelize.define. Our User model looks like this:
var User = sequelize.define('user', {
firstName: {
type: DataTypes.STRING,
allowNull: false,
unique: 'compositeIndex'
},
lastName: {
type: DataTypes.STRING,
unique: 'compositeIndex'
},
.........
.........
.........
dateJoined: {
type: DataTypes.DATE,
defaultValue: DataTypes.NOW
}
}, {
getterMethods : {
address: function() { return this.state + ', ' + this.country }
},
setterMethods : {
address: function(value) {
var names = value.split(', ');
this.setDataValue('country', names[0]);
this.setDataValue('state', names[1]);
},
}
});You just need to define the columns and their data types and Sequelize will automatically add createdAt and updatedAt to your model. There are a few other settings you can also configure for your columns.
- allowNull — Set false if null is not allowed
- defaultValue — Set a default value for a column.
Example:DataTypes.NOWfordateJoinedcolumn. - autoIncrement — Automatically increments the column by one every time a new row is inserted
- comment — Mention a comment for your column
- unique — Mention a boolean true to define a column as unique. For a composite key, a string can be mentioned for multiple columns.
Example
userId: {type: Sequelize.STRING, unique: true},
fullName: { type: Sequelize.STRING, unique: 'compositeIndex'},
dob: { type: Sequelize.DATE, unique: 'compositeIndex'}Getter and setter methods
In Sequelize, we can define pseudo properties on a model. These properties are not an actual part of the database schema, they are just for the models. In the example above, “address” is a pseudo-property, and its value is initialized through getter and setter methods. When state and country are fetched from db, Sequelize merges them with a comma to populate the “address” property (getterMethods). Similarly, when we set the address, it gets split into state and country (setterMethods). Thus, the “address” seems like a column in db but actually it’s not.
Preparing sample data
There are different approaches to create a new entry in DB. The first approach is to build a non persistent object and then call save() to persist the data.
var newUser = user.build({
firstName: 'John',
lastName: 'Doe',
age: 28,
country: 'US',
state: 'Indiana',
email: '[email protected]'
});
newUser.save().then(function() {
// Do stuffs after data persists
})Another alternative is to do both the steps in a single line using user.create({.....}).then(function(user) {}). If we need to create bulk instances, here’s how we do it.
user.bulkCreate([USERS],{ validate: true }).then(function() {
// Congratulate user!
}).catch(function(errors) {
// Catch if validation failed
// Print errors
});Check ./routes/createData.js in the sample project for the bulk creation logic. Go with the steps on localhost:3000 to see the operations live as we discuss further.
Querying data
We can query data using findAll and findOne which takes additional parameters like attributes, where condition, ordering, and pagination. Let’s learn these through examples.

Get first 100 user instances. The highlighted column in the image above comes from the “group” table.
user.findAll({limit: 100}).then(function(users) {
// Send array to view
});Get user by email
user.findOne({where : {email: '[email protected]'}}).then(function(user) {
// Send user to view
});A little more complex example. Find all users of California and Arizona whose age is in between 20 and 40 and last name contains ‘user’.
var query = {};
query.where = {
$or: [
{state: "California"},
{state: "Arizona"}
],
age: {
$between: [20, 40]
},
lastName: {
$ilike: '%user%'
}
};
user.findAll(query).then(function(users) {
// Do something awesome here
}); SELECT "id", "firstName", "lastName", "email", "age", "country", "state", "dateJoined", "createdAt", "updatedAt"
FROM "user" AS "user"
WHERE ("user"."state" = 'California' OR "user"."state" = 'Arizona')
AND "user"."age" BETWEEN 20 AND 40
AND "user"."lastName" ILIKE '%user%';If you need more operators for querying data, you can find the list on the net.
Sequelize also offers an option to directly provide SQL query, like:
sequelize.query(QUERY, { model: user }).then(function(users) {
// Array of instance of user
})Updates and destroy
Updating an instance can take two parameters, the updated values and where condition.
user.update({
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
address: "Nevada, US"
},{
where: { email : "[email protected]" }
})
.then(function () {
});“Destroy” also takes a where condition (Check below). You can also follow the callback syntax (just like update) to do some logic after destroying.
user.destroy({
where: {
email: '[email protected]'
}
});
// DELETE FROM user WHERE email="[email protected]";Relation and associations
In this section, we will learn about one-to-one association. When two models are linked to each other by a single foreign key, we say it as a one-to-one association. In our case, we have two models: user and group. Each user is associated with a single group. So the user model has a foreign key group_id which points to the groupIdof the group model. Defining this association is very easy in Sequelize.
user.belongsTo(group, {foreignKey: 'group_id', targetKey: 'groupId'});Once the line above is executed, it creates a foreign key “group_id” for the group model. To read the data from both tables (like join in SQL), simply include the target model as follows:
user.findAll({
limit: 100,
include: [{
model: group
}]
}).then(function(users) {
// Send users to view
});Wrapping up
There are more features in Sequelize, such as transaction management, hooks, scopes, etc. Combining all these features Sequelize becomes a strong ORM module for Node.js.
But when it comes to complex relations and associations, it seems a little dimmed and maintainability could be a concern. But other than that it is a bullet-proof module with well-described documentation.
Lastly, if ever you feel the need to learn more about technologies, frameworks, languages, and more – InApps will always have you updated.
List of Keywords users find our article on Google
[sociallocker id=”2721″]
| typeorm schema |
| sequelize |
| orm 2022 |
| typeorm |
| crud admin generator |
| orm node |
| custom healthcare software development indianapolis |
| node orm |
| localhost 3000 |
| postgresql create function |
| hire mariadb developers |
| sequelize where |
| custom healthcare software development company indianapolis |
| sequelize node js |
| sequelize nodejs |
| email to custom object |
| npm express |
| node sequelize |
| sequelize migration |
| postgresql wikipedia |
| node pg |
| sqlite alternatives |
| offshore software development services company indianapolis |
| offshore software development indianapolis |
| why do companies outsource software development indianapolis |
| software development outsourcing indianapolis |
| sequelize findone |
| indiana tech niche |
| sequelize datatypes |
| sequelize findall where |
| sequelize data types |
| custom software development services indianapolis |
| sequelize delete |
| sequelize define |
| software development methodologies indianapolis |
| sequelize js |
| java software development company indianapolis |
| custom software development companies in california indianapolis |
| express vs nestjs |
| typeorm postgres |
| sequelize orm |
| recruiters guide to ats data migrations |
| postgresql saas |
| foreign key postgres |
| sequelize npm |
| npm pg |
| sequelize update |
| game ui database |
| sequelize vs typeorm |
| ilike products |
| many to many typeorm |
| typeorm create |
| object relation mapping |
| typeorm insert |
| mssql wiki |
| nestjs typeorm |
| sequelize validate email |
| sequelize get data |
| object relational mapping |
| sequelize save model |
| what is sequelize |
| ilike |
| postgres string function |
| typeorm transaction |
| make a phone call node.js |
| object oriented software engineering indianapolis |
| postgresql foreign key |
| sequelize documentation |
| nestjs tutorial |
| what is nestjs |
| postgres foreign key |
| one to one sequelize |
| react native crud mysql |
| user story mapping |
| sequelize composite foreign key |
| nestjs best orm |
| rm es |
| software development company website template free indianapolis |
| orm twitter |
| sequelize query |
| sequelize include where |
| sequelize findall |
| wikipedia great gatsby |
| introduction to java wikipedia |
| goodfirms reviews |
| sequelize join |
| sequelize bulk update |
| sequelize foreign key |
| vision net company wikipedia |
| bulk create in sequelize |
| find or create sequelize |
| sequalize update |
| typeorm relations |
| sequelize include 2 models |
| typeorm findone |
| postgresql youtube |
| where sequelize |
| saas catch can |
| sequelize.define is not a function |
| update sequelize |
| sequelize get foreign key object |
| sequelize transaction |
| gatsby ecommerce starter |
| sequelize find like |
| nestjs populate |
| newrow tech check |
| sequelize insert |
| sequelize pagination example |
| sequelize relationships |
| sequelize.query |
| sequelize include attributes |
| operator sequelize |
| typeorm one to many |
| typeorm relations example |
| what is typeorm |
| crud typeorm |
| dotenv alternatives |
| express sequelize mysql example |
| mariadb comment |
| orm |
| postgresql mailing list |
| sequelize custom query |
| typeorm errors |
| sequelize attributes include |
| }) |
| twitter to postgresql |
| go orm |
| typeorm is not null |
| db method app |
| sequelize view model |
| pagination npm |
| sequelize create |
| where or sequelize |
| typeorm migration foreign key |
| typeorm or query |
| where in typeorm |
| belongsto sequelize |
| ifnull postgres |
| nestjs get |
| attributes in sequelize |
| sequalizer |
| sequelize where condition |
| orm software |
| sequelize find one |
| nestjs delete |
| postgres update multiple tables |
| mssql function |
| npm schema |
| sequelize doc |
| express with sequelize |
| node orm mysql |
| sequelize pagination |
| crud nestjs |
| object-relational mapping |
| .then is not a function |
| default value sequelize |
| dotenv alternative |
| node.js postgresql crud example |
| postgres list function |
| typeorm with postgres |
| where and sequelize |
| node js sequelize tutorial |
| postgres hooks |
| react native persist |
| sequelize attributes |
| sequelize model include |
| sequelize where is null |
| call user func array expects parameter 1 to be a valid callback |
| nestjs adalah |
| nestjs template engine |
| node-pg |
| postgres boolean |
| sequilize |
| typeorm delete |
| nodejs findall |
| orm website |
| postgres keywords |
| transaction management wiki |
| ejs vs react |
| mysql split string by comma |
| nestjs transform |
| nodejs orm |
| now() in postgres |
| postgres function examples |
| sequelize model |
| set column postgres |
| typeorm like |
| business objects tutorial for beginners |
| callback software for saas |
| foreign key mariadb |
| node orm postgres |
| npm query-string |
| sequelize is not associated to |
| ej’s tanning |
| hire sqlite developers |
| npm install sequelize |
| npm mysql2 |
| postgresql synchronization |
| sequelize validate |
| callback apps for real estate |
| nestjs mssql |
| postgres hot update |
| postgres where in string |
| react-native-background-upload |
| sql query to send email |
| good name for software development company indianapolis |
| nestjs mysql example |
| node red database connection |
| npm pg-native |
| orm column |
| postgresql if function |
| postgresql ifnull |
| update column postgres |
| createdat sequelize |
| great gatsby map |
| postgres default value |
| react admin pagination |
| sequelize in |
| sql find object by name |
| update join sqlite |
| define pseudo- |
| dotenv nodejs example |
| ejs express |
| mariadb create table syntax |
| nestjs tuto |
| object-oriented databases reviews |
| array contains postgres |
| ejs print array |
| express template ejs |
| gatsby awesome pagination |
| mariadb string contains |
| mysql schema synchronization |
| postgres array |
| postgres list table columns |
| postgresql array functions |
| postgresql update column from another column |
| react native send email in background |
| timescale db |
| localhost://3000 |
| node postgres orm |
| npmjs mysql |
| postgres delete join |
| team validation failed |
| ats save file location |
| define pseudo |
| delete column postgres |
| express vs nest js |
| jade nodejs |
| localhost:3000 |
| node js orm |
| npm install psql |
| npm postgres |
| postgres age function |
| postgres array function |
| sequelize model belongsto |
| what is an orm |
| best node orm |
| game object |
| sqlite synchronization |
| ejs template in node js |
| gatsby starter |
| getter app |
| golang orm |
| js orm |
| pseudo boolean function |
| sequelize mysql |
| sql orm for node js |
| sqlite boolean |
| date function postgres |
| db 5 column |
| emailage |
| postgres app |
| sqlite mysql postgresql |
| autoincrement |
| relational |
[/sociallocker]
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.