- Home
- >
- Offshore News
- >
- An Overview on Vietnam Software Industry Update
As the world increasingly relies on digital solutions, the software industry has become a cornerstone of economic development. Vietnam, a rising star in the global tech scene, has seen significant growth in its software industry over the past few years.
This blog will provide a comprehensive overview of the Vietnam software industry in 2025, highlighting key statistics, trends, and factors driving this dynamic sector. This guide guarantees to offer valuable insights into Vietnam’s burgeoning software landscape.
Key Summary
1. Vietnam Software Industry Overview
- ICT Revenue (2022): Reached $148 billion, up 8.7% from 2021; projected to hit $165 billion in 2023 despite a first-half dip due to global economic challenges.
- Sector Contributions: Hardware ($136 billion), software/IT services ($13 billion).
- Growth Rate: The ICT sector grew at 8.8% in 2022, outpacing national GDP; it peaked at 10.84% in 2020 (2016–2022).
- Digital Firms: 67,311 firms, including 5,097 hardware, 18,162 software, and 767 digital content firms.
- National Digital Transformation: Over 1.39 billion transactions via government service platform; 849,290 SMEs in digital transformation program (as of June 2023).
- Microchip Ecosystem: Investments from Intel and Samsung; supported by 50+ domestic firms and 5,000+ Vietnamese engineers to enhance the global microchip value chain role.
2. Factors Driving Growth
2.1 Skilled Workforce
- Demographics: Predominantly Gen Z/Millennials; 29.8% aged 20–24, 26.2% aged 25–29.
- Geographic Distribution: Ho Chi Minh City (56.7%), Hanoi (33.8%), Da Nang (5.7%).
- Experience Levels: 52.8% with 0–3 years (25.1% 0–1 year, 27.7% 2–3 years), 26.7% with 4–7 years, and 20.5% with 7+ years.
- Skill Levels: 45% fresher/junior, 28% middle, 20% senior, 7% leaders.
- Global Ranking: Vietnamese developers ranked 23rd globally (HackerRank 2023), 2nd in freelance quality after the USA, and among the top 10 worldwide.
2.2 Competitive Costs
- Low Labor Costs: Mid-range salaries ($1,100–$1,500/month) dominate in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi; higher salaries ($600–$1,000) are more common in Hanoi.
- Cost Advantage: Makes Vietnam attractive for software development outsourcing.
2.3 Increasing Foreign Investment
- FDI (2023, 8 months): $18.15 billion, up 8.2% from 2022; Singapore ($3.83 billion, 21.2%), China ($2.69 billion, 14.8%), Japan ($2.58 billion, 14.2%).
- FDI (2022): $22.48 billion; Singapore (23.3%), South Korea (17.6%), Japan (17.3%).
- Key Regions: Hanoi ($1.87 billion), Ho Chi Minh City (38.9% of new projects).
- Impact: Boosts economy, enhances tech infrastructure, and supports software industry growth.
3. Challenges
3.1 Economic Downturn
- Impact: Hiring freezes, layoffs, reduced IT budgets, and delayed/canceled projects decrease job opportunities and intensify competition.
3.2 Need for Highly Skilled Developers
- Skills Gap: Young developers lack soft skills (communication, teamwork, problem-solving) and practical business knowledge.
- Language Barriers: Limited proficiency in English, Chinese, Japanese, or Korean hinders collaboration with international clients.
3.3 Employee Retention and Salary Expectations
- Issue: High turnover after training; rising wages, especially for web developers, increase expectations.
- Solution: Fair, transparent salary policies and healthy work environments to retain talent.
3.4 Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Challenges: Automation reduces demand for routine tasks (e.g., data entry, basic analysis).
- Opportunities: Growing need for AI system developers, data managers, and professionals with human-centric skills (creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence).
4. Key Trends in 2025
4.1 Rise of AI and Machine Learning
- Trend: Local firms invest in AI-driven solutions (chatbots, analytics), with increased R&D focus.
4.2 Growth of Fintech
- Driver: Large unbanked population, rising smartphone use.
- Impact: Fintech startups innovate in digital payments, lending, and financial management, boosting the software industry.
4.3 Emphasis on Cybersecurity
- Priority: Digital transformation increases demand for cybersecurity solutions and professionals.
4.4 Remote Work Trends
- Shift: Hybrid work is popular, offering flexibility; full office work remains dominant (3.5% fully remote).
- Challenge: Companies adapt to manage and engage remote/hybrid teams effectively.
1. Vietnam Software Industry Overview
ICT Revenue (2016-2023)
The communications and information sector in Vietnam has shown a significant growth trajectory, reaching $148 billion in 2022, an 8.7% increase compared to 2021. Despite a drop in the first half of 2023 due to global economic challenges and reduced IT product consumption, the forecast for the entire year remains optimistic at $165 billion. Hardware contributed significantly, with $136 billion, while software and IT services added $13 billion. The ICT sector’s growth rate of 8.8% outpaced national GDP growth, highlighting its importance in the economy.
Vietnam GDP & ICT Sector Growth Rate
Vietnam’s ICT sector has consistently outpaced GDP growth, with a growth rate of 8.8% in 2022. From 2016 to 2022, the ICT growth rate varied, reaching a peak of 10.84% in 2020.

Vietnam IT Industry Growth. Source: TopDev Report
Vietnam software industry boasts 67,311 digital technology firms, which include:
- Hardware Firms: 5,097
- Software Firms: 18,162
- Digital Content Firms: 767
National Digital Transformation
As of June 18, 2023, over 1.39 billion transactions have been conducted through the national government service platform. Additionally, 849,290 enterprises have participated in the SME digital transformation support program.
Building a Supporting Ecosystem for Microchip Technology
Vietnam is actively fostering an ecosystem to support chip manufacturers, with investments from global giants like Intel and Samsung. This effort aims to elevate Vietnam’s role in the global microchip value chain, supported by over 50 domestic enterprises and more than 5,000 Vietnamese engineers.
2. Factors Driving the Growth of Vietnam Software Industry
2.1 Skilled Workforce of Vietnam Software Industry

Age Distribution Of Developers In Vietnam
Most developers in Vietnam Software Industry are Gen Z and Millennial generations, with a significant portion aged between 20 to 34 years old. Specifically, the largest age group in the IT market is 20-24 years old, accounting for 29.8% of developers, followed by the 25-29 age group at 26.2%. Most developers are concentrated in Vietnam’s two largest cities: Ho Chi Minh City (56.7%) and Hanoi (33.8%). Additionally, cities like Da Nang are also emerging as notable tech hubs, housing 5.7% of the developer population.
More than half of the developers have up to three years of experience in IT jobs, with 25.1% having 0-1 year and 27.7% having 2-3 years of experience. This indicates a vibrant and expanding entry-level workforce, continuously infused with new talent. Furthermore, 26.7% of developers have 4-7 years of experience, and 20.5% have over seven years, showcasing a blend of fresh talent and experienced professionals capable of mentoring and leading projects.
The Vietnam IT Market Report by TopDev also indicates that more than 45% of developers are at the fresher to junior level. Meanwhile, 28% are at the middle level, and senior developers make up nearly 20% of the workforce. Leaders and higher-level professionals account for 7%.
In terms of skill, Vietnamese developers are ranked among the top 10 in the world, following countries like the USA, UK, and France. In the world ranking of best freelancers, Vietnam is second only to the USA. This means Vietnamese freelance developers are highly regarded and trusted for their quality work. According to HackerRank’s 2023 report, Vietnamese developers are ranked 23rd in the world.

Which country has the best developers? HackerRank.
2.2 Competitive Costs of Vietnam Software Industry
Low labor costs make Vietnam an attractive destination for software development and other IT services. Ho Chi Minh City has a relatively balanced distribution of IT salaries across various ranges. A higher percentage of IT professionals earn mid-range salaries, between $1,100 and $1,500 per month. Meanwhile, in Hanoi, there is a higher concentration of IT salaries in the mid-range ($1,100 – $1,500) and the higher range ($600 – $1,000). Similar to Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi shows relatively lower percentages of salaries in the extreme ranges.

Developer Salary Overview – Vietnam Software Industry
2.3 Increasing Foreign Investment
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in the growth and development of Vietnam software industry. The influx of capital from foreign investors not only boosts the local economy but also enhances the technological capabilities and infrastructure needed for the industry to thrive. Here are some key points regarding FDI in Vietnam:
In the first eight months of 2023, Vietnam received $18.15 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI), which is 8.2% more than the same period in 2022. This increase shows that Vietnam is a good place for investors. Singapore invested the most, with $3.83 billion, making up 21.2% of the total FDI. China contributed $2.69 billion, accounting for 14.8% of the total, while Japan added $2.58 billion, which is 14.2% of the total FDI. Other significant investors included South Korea and Hong Kong.
In 2022, Vietnam received nearly $22.48 billion in FDI. The main investors were Singapore, which invested $6.46 billion (23.3% of the total), South Korea with $4.88 billion (17.6%), and Japan with $4.78 billion (17.3%).
Hanoi attracted the most foreign investment, with a total of $1.87 billion. Meanwhile, Ho Chi Minh City had the most new projects, making up 38.9% of the total. These trends show that foreign investors are very interested in Vietnam, which helps the country’s economy grow, especially in the IT and software industries.
3. Challenges of the Vietnam Software Industry
Opportunities don’t come without challenges. Here’s a closer look into core challenges that will shape the Vietnam software industry.
3.1. Economic Downturn Is Challenging Vietnam Software Industry
Economic downturns have a profound impact on the Vietnam software market. Many organizations implement hiring freezes or reduce their workforce through layoffs, leading to a decrease in IT job opportunities. Reduced IT budgets mean less spending on IT projects and initiatives, decreasing the demand for IT professionals.
Economic uncertainty can cause companies to delay or cancel planned IT projects, especially those requiring significant investments. As a result, the competition for available IT roles becomes more intense, making it harder for professionals to secure new job opportunities.
3.2. Need for More Highly-Skilled Developers
The demand for senior and experienced developers is growing due to tighter salary budgets and increasing business requirements. However, there is a notable skills gap in the industry. Many young, talented developers lack soft skills such as communication, teamwork, self-organization, and problem-solving, which are crucial for efficient working.
Also, practical business knowledge is essential for developers to understand client needs and contribute effectively to project outcomes. Language barriers also pose a challenge, as many Vietnamese developers may not have the proficiency required to work with international clients or collaborate with teams in other countries. Skills in foreign languages like English, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean are highly sought after by many foreign tech companies.
3.3. Retention of Employees and High Salary Expectations
This is a common scenario in any software industry, including the Vietnam software industry. Companies invest in training new hires, only to see them resign once they gain enough experience. The tech industry has seen a considerable rise in average wages, with web developers and trendy roles experiencing the most significant increases. This competitive job market allows job seekers to choose employers who meet their salary expectations.
To address this, employers should offer fair and transparent salary policies that cater to the needs of their workforce. Providing a healthy work environment with fair compensation practices is crucial for promoting the well-being of both parties.
3.4. Rising of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The rise of AI presents both opportunities and challenges to information technology in Vietnam. Automation of routine tasks may decrease the demand for jobs involving manual data entry, basic analysis, or rule-based decision-making. However, there is an increasing demand for individuals who can develop, implement, and maintain AI systems and algorithms. The creation of new positions focused on managing and maintaining AI systems is essential.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on human-centric skills such as creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and complex decision-making. Professionals who can collect, clean, manage, and analyze large volumes of data are in high demand to ensure the quality and accuracy of data used in AI systems.
4. Key Trends of Vietnam Software Industry in 2025
4.1. Rise of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are gaining traction in Vietnam Software Industry. Many local companies are investing in AI-driven solutions, from chatbots to advanced data analytics. This trend is expected to continue, with significant investments in AI research and development.
4.2. Growth of Fintech
The fintech sector in Vietnam is booming, driven by a large unbanked population and increasing smartphone penetration. Local fintech startups are developing innovative solutions for digital payments, lending, and financial management, contributing to the overall growth of the software industry.
4.3. Emphasis on Cybersecurity
With the rise in digital transformation, cybersecurity has become a top priority in Vietnam’s technology industry. Vietnamese companies are increasingly focusing on enhancing their cybersecurity measures, leading to a surge in demand for cybersecurity solutions and professionals.
4.4. Remote Work Trends
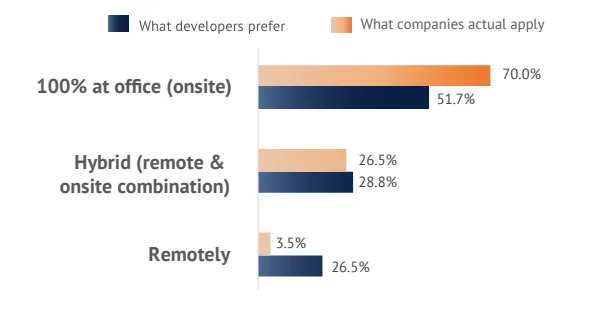
Hybrid working has become very popular this year, giving developers more flexibility. Even though many developers like it, companies are still figuring out how to manage and engage employees effectively. Right now, working entirely in the office is still the most common for tech developers. In comparison, fully remote work makes up only 3.5% of jobs in the market.
Let’s create the next big thing together!
Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.